Interesting information has come forth, something that the Iranian people have known for years, but the west is only finding out now.
I am reprinting this article in full, with the full permissin of the author.
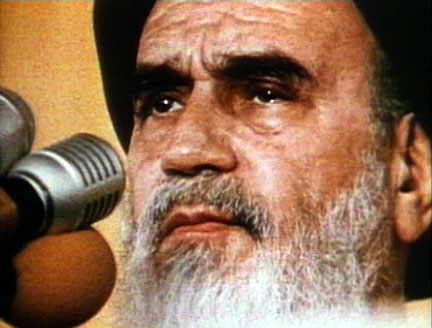
The world must know, the man behind the Islamic revolution in Iran, was not even an Iranian!
AntiMullah.com
The Clerics Lash Back as Iranians question their legitimacy
DEFENSE & FOREIGN AFFAIRS STRATEGIC POLICY 3, 2004
Iran By Alan Peters, Contributing Editor
The Clerics Lash Back as Iranians Question Their Legitimacy
VIGOROUS ATTACKS ON THE CREDIBILITY and legitimacy of the clerical leadership in Iran have continued to mount since the February 20, 2004, Majlis (Parliament) elections which, despite the removal of so-called reformists from the ballot, still failed to attract a meaningful voter turn-out. The elections showed the extent of electoral fraud to which the clerics were forced to turn, highlighting their tenuous hold on power.
There are now signs that the underpinnings of the clerics will be attacked still further, especially as evidence is now available showing even that their claims to religious authority are open to question.
The late Soviet leader Joseph Stalin once said: Its not who votes, but who counts the votes, a maxim which has found resonance in the February 20, 2004, Iranian national elections. A substantial cadre of ballot officials, directly answerable to the hard-line clerical leadership of Supreme Leader Ali Hoseini-Khamenei, counted the votes and issued results which almost nobody in Iran or abroad really believed to be accurate. 2
The credibility of the February 20, 2004, elections was essentially further undermined when observers saw already half-filled ballot boxes stuffed with fake votes transferred into polling stations on election day, and artificial crowds created by reducing the number of available ballot boxes at each location to create long lines and the appearance of a large turnout.
This deception was bolstered by rent-a-crowd groups of black chadored women who were called into action when any one of the 300 foreign journalists, covering the elections, appeared at a polling station.
Tehran sources report that 54 full ballot boxes disappeared and that initially the Interior Ministry offered correct voter turnout figures showing an attendance of about 11 percent in Tehran. This task was taken away from the Interior Ministry and the tally given as more than 30 percent for the capital and a touch more than 50 percent for the nation.Missing from all statistics are the huge number of blank votes cast by Government employees and students forced to vote to receive a voted stamp in their ID cards, without which they could face future difficulties.
Reformers and opposition groups of all kinds, including the leftist Iran Mujahedin Organization calculated that the hardliners only truly had the support of about 10 to 15 percent of Irans voters. What bears watching more than the struggle between the hardliners and the so-called reformers is the turmoil, rising from the political depths, which threatens to destabilize the status quo in Iran far beyond the earlier student unrest and which now targets the legitimacy of the Islamic coup itself.
Reformers, with nothing left to lose and outraged by the disqualification of their candidates and the resultant takeover by the hardliners of the only nationally- elected government body, have begun to poise an attack at disqualifying the ruling clerics claim to any legitimacy; to even be in power, let alone rule. Diplomatic sources speculate that a significant nudge in this direction could well result in a speedy downfall of the Iranian clerics.
Supreme Ruler Ali Khameneis authority and ability to govern has been publicly and directly questioned in an unprecedented open letter written by members of the Majlis (parliament) and widely publicized outside Iran. Two Iranian newspapers, Yaass Noh and Shargh, which reprinted the letter within the country, were immediately closed down. This essentially unprecedented confrontation against the clerical leadership of Iran signaled an attempt to cut the clerics off at the knees rather than dispute election details or the misuse of existing power structures.
Nor are the hardliners still a monolithic group, sharing the same religious and ideological aims and opinions as was the case when Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini was alive and in charge after the 1979 collapse of the Imperial Government. Khomeini had demonstrated an unbending, single-minded resolve and capability to hold all institutions and individuals in line, but now, previously concealed dissent among the major players has sprung to the fore.When the veil of democratic and fair elections was torn away by the hardliners, it revealed more than was intended.
Significantly, the former President of Iran and head of the Expediency Council and international businessman Ayatollah Abbas Hashemi Rafsanjani has also openly announced his policy disagreement with Ali Khamenei over talks with the US, citing sorrow that Khameneis clinging to Khomeinis anti-US edicts rather than to pragmatic policy, had stifled Irans ability to advance politically.
Religious scholars can find no basis for Ali Khameneis self-awarded ayatollah title nor of Rafsanjanis use of that appellation. Nor Khomeinis, though he was artificially elevated and granted use of Ayatollah to save his life.
With all bets off, the reformers have now struck at the heart of the revolution and are insisting on an inquiry into the disappearance of Grand Ayatollah Mussa Sadr, some 25-years ago, during a visit to Libya.3

The Iranian born leader of the Lebanese Shia was revered and respected above all others in the Shia world. He refused to accept Ruhollah Khomeini as an ayatollah and with the influence Mussa Sadr enjoyed, he became an insurmountable obstacle to Khomeinis political plans, and of those who supported the overthrow of the Shah and needed a despot like Khomeini to be their cats paw.
Grand Ayatollah Sadrs mysterious disappearance in Libya, his body was never found, opened the way for Khomeini to invade Iran, which accurately describes the action of a foreign national taking over a country in which he was neither born nor had any Persian blood in his veins at all, paternally or maternally. While one devout Iranian in California speaks of Khomeini reverently as a great man, similar to Hitler, other less friendly Persians liken him to an invader like Genghis Khan, 12. the Mongol scourge.
Unable to strike at the hardliners on an uneven playing field, the reformers have now begun an all-out assault on their former clerical allies. The cornerstone and founder of the Islamic Republic of Iran, from which the present leaders draw their legitimacy to govern, was Khomeini and the structure which he put in place. However, there is compelling evidence that Ruhollah Khomeini was never an Iranian in the first place and had no right to inflict his policies on the Iranian people.
Nor was his elevation to the title of ayatollah anything more than a political, face-saving expediency to prevent his being hanged for treason in 1964. Considerable effort was made in 1979 to eradicate evidence of any record of either Khomeinis non-Iranian origins and the source of his use of the title of ayatollah, and one of the first actions which Khomeini took,within hours of his return to Iran after the Shah left, was to execute two prominent men who were living proof of his origin and also of his false ayatollah status.
One of these was Gen. Hassan Pakravan, Head of SAVAK, the Imperial Iranian national intelligence and security organization.

Furthermore he immediately tried to assassinate the highly-respected Ayatollah Shariatmadari, who, with Ayatollah Golpayegani, had in 1964 granted Khomeini the false title. They had agreed to allow Khomeini then literally awaiting death on charges of treason to be called an ayatollah to save his life: it was forbidden to execute an ayatollah. This took place in 1964 at the urging of the British Ambassador to Iran and Gen. Pakravan, when a face-saving legal reason had to be found not to hang Khomeini for treason. It is known that Pakravan had fought hard to avoid Khomeinis execution at that time.
Later, when the 1979 assassination attempt failed against Shariatmadari, Shariatmadari, far higher in the religious hierarchy than Khomeini, was placed, incommunicado and under house arrest, without the right to preach or receive visitors other than a handful of close relatives, whose anti-Khomeini statements could be easily impugned as biased.
Recent reports from Tehran showed the death fatwa (religious edict or opinion) issued against British author Salman Rushdi by Khomeini for writing an anti-Islamic book and cancelled a few years ago, had been reinstated to warn journalists or writers the clerics cannot directly control, that they risked death at the hands of devout Moslem fanatics if they uttered a word against the rulers in Iran or weakened their standing by revealing the illegitimate provenance of their power and thus contest their right to impose their theocratic despotism on a reluctant people.
Few contest that Khomeinis mother was a Kashmiri Indian, but even fewer Iranians or otherwise know his fathers origins or his real name. The late Iranian Senator Moussavi, who represented Khuzestan Province in Southern Iran, at the time of the monarchy, knew Khomeinis father and his four sons well, looked after their needs, used his influence to obtain their Iranian identity cards with fictitious dates and places of birth to avoid military service. Sen. Moussavi died for this help, on Khomeinis personal orders, immediately on this mullahs return from France after the 1979 coup.
SAVAK chief Gen. Pakravan, the man who saved Khomeinis life in 1964, was taken that same night onto the roof of his house and shot to death for having compiled a complete background file on Khomeini.
The SAVAK background file still exists, as a senior SAVAK official, who defected and joined SAVAMA (the clerics equivalent of the SAVAK) took possession of it. This same man was reportedly head of SAVAMA in the US for quite some time, and sources indicate that he has kept the file for a rainy day.
Why did Khomeini return to Iran with such a bloodthirsty mind set? It seems clear that it was to exact the revenge which he said he would have. Prior to his return to Iran in 1979, Khomeini openly stated that he would kill as many Iranians he considered everyone in Iran guilty in advance as there were hairs on the head of his son, killed in a car accident, but in his mind killed by Iranian authorities.
Unable to provide an acceptable paternal background for Khomeini, a story was concocted to link his paternal heritage to that of his Kashmiri Indian mother and introduced an Indian-born father (also from Kashmir) but of Iranian heritage. In fact, no such person existed. But someone with similar and misleading characteristics certainly did, which could lend credence to this fiction of an Indian father.
Khomeinis real father,William Richard Williamson, was born in Bristol, England, in 1872 of British parents and lineage. This detail is based on first-hand evidence from a former Iranian employee of the Anglo- Iranian OilCompany (later British Petroleum: BP), who worked with and met the key players of this saga. This fact was supported by the lack of a denial in 1979 by Col. Archie Chisholm, a BP political officer and former editor at The Financial Times, when interviewed on the subject at his home in County Cork, Ireland, by a British newspaper.
The then-78-year old Chisholm stated: I knew Haji [as Williamson was later known] well; he worked for me. He certainly went native but whether he is Khomeinis father I could not say. Would not an outright, ridiculing denial have been the natural response, were there no truth to the British paternity? From someone who knew Haji [and thus the truth] well?
Chisholm obviously wished to avoid a statement leading to political controversy or possible personal retribution in the very year Khomeini took over in Iran. Nor as a former, experienced political officer himself would he be willing to drag Britain into the new Middle East conflict. But neither was he prepared to provide an outright lie instead of his no comment.
How it all happened:
A stocky, handsome, dark-haired Bristol boy, Richard Williamson ran away to sea at the age of 13 as a cabin boy, on a ship bound for Australia. However, he jumped ship before he got there. Little is known about him until he showed up, at the age of 20, in Aden at the Southern end of the Arabian Peninsula in South Yemen, where he joined the local police force.
His good looks soon had Sultan Fazl bin-Ali, ruler of Lahej, persuading him to quit the police force to live with him. Richard later left him for another Sheikh, Youssef Ebrahim, a relative of the Al- Sabah family, which rules Kuwait today.
A few points should be remembered about the PersianGulf and Arabian Peninsula area at that time. Regional countries like Lebanon, Iraq, Jordan, Syria, Saudi Arabia and so forth did not exist as sovereign entities and were artificially created about 70 years ago by the British and French governments when they partitioned the area. Iran, or Persia as it was called, was soon to be controlled by Russian Cossacks in the North and the British Army in the South, although technically it remained an independent monarchy under the largely absentee Qajar dynasty.
British military presence in Iran was under Lt.-Col. Sykes (later Sir Percy Sykes), based in Shiraz, but politically controlled by Sir Arnold Wilson in Khorramshahr (then called Mohammareh) with assistance from E. Elking- ton in Masjid-Suleiman and Dr Young, based in Ahwaz. All three were cities in Khuzestan Province, which was later represented by Senator Moussavi. Col. T.E. Lawrence, who gained fame as Lawrence of Arabia, operated out of Basra in Mesopotamia (Iraq) and Khorramshahr during this same period.
Oilfields, far beyond the technological capability of the Arab tribes (or Persia) to develop or appreciate as a valuable commodity, were being discovered and exploited by the British, including via the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company, formed to siphon off oil from Khuzestan Province in Southern Iran.
Kuwait, on the other side of the Persian Gulf was still not a country at the time. As the major player in the Middle East oil industry, Britain had to exert influence and control through its political and oil personnel. Haji Abdollah Williamson became one of these in 1924 when he joined British Petroleum as political officer. He retired under that same name in 1937, at the age of 65. Earlier, in what is now Kuwait, Richard Williamson had very quickly converted to Islam and adopted the first name of Abdollah. Family names were still unusual and son of the son of or son of a type of worker or craftsman was still commonly used to identify people. For 14 years he had lived among the Bedouin tribes on the Arabian Peninsula and in 1895 and 1898 he went on pilgrimages to Mecca, took on the rightful title of Haji and took on his first benefactors name of Fazl, adding Zobeiri to it as a distin- guisher. Thus William Richard Williamson became Haji Abdollah Fazl Zobeiri.
During his service with British Petroleum in the Persian Gulf, Haji Abdollah took his vacations in Indian Kashmir, to rest from the relentless Gulf heat and in this timeframe married at least seven times to Arab and Indian women each under Muslim marriage rituals. He sired 13 children of whom seven were boys and the rest girls with most of the children dying in early childhood. His repeated Kashmir excursions and Indian wives and use of the name Abdollah Fazl Zobeiri probably give rise to the Kashmir Indian father misconception.
With dark-haired Haji Abdol- lah a fanatically devout Muslim, a characteristic he imposed on his children, this fervent religious attitude and Arab nomenclature would not normally be an expected combination for a foreigner, especially an Englishman. He insisted his four surviving sons attend religious school in Najaf (in Iraq) under the tutelage of Ayatollahs Yazdi (meaning of the city of Yazd) and Shirazi (of the city of Shiraz). Two of them, Hindizadeh (meaning Indian born) and Passandideh (meaning pleasing or approved) studied well and eventually became ayatollahs in their own right.
The third boy, a troublesome young man, failed to make his mark in Najaf and went to the Iranian holy city of Qom, where he studied under Ayatollah Boroujerdi. When family names became a requirement by law under His Majesty Reza Shah, the young man chose the city of his residence Khomeinas the designator and took on the name Khomeini (meaning of Khomein).
The fourth son hated theology and went across the Persian Gulf to Kuwait and opened up two gas (petrol) stations using the paternal family name of Haji Ali Williamson, though it is unclear if he ever performed the Haj pilgrimage. This in itself links Khomeini through that brother with Haji Williamson. Why, otherwise, would Rouhallah Khomeinis undisputed brother use the Williamson family name? The patriarch of this brood, Haji Abdollah Fazl Zobeiri (aka Haji Abdollah Williamson in BP), was thrown out of Iran by Reza Shah along with three other British political officers for anti-Iranian activity and joined his son in Kuwait. Here he took on the duties of Oil Distribution for the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company.
With his longstanding contacts in the Arab world and his Muslim religion, he forced a 50/50 agreement between US oil interests in Kuwait and the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company as well as in 1932 pursuing the exclusive exploration rights for British Petroleum in Abu Dhabi.
His lack of a formal education forced British Petroleum to send out Archie H. T. Chisholm (see above), a senior executive, to conclude the Abu Dhabi contract and together with Haji Abdollahs political influence they overcame competition from Major Frank Holmes, Sheikh Hussein and Mohammad Yateen to successfully land the exclusive contract. Chisholm, as he said, got to know Khomeinis father well. Back in Iran again in 1960, Khomeini saw an opportunity to exact revenge for his father having been thrown out of Iran and to impose his Islamic fundamentalist philosophy onto an Iran struggling with budget problems, caused mostly by its oil being in the control of foreign oil companies, which decided not Iran how much oil the country was allowed to produce and at what price it had to be sold.
With his own and his familys theological background, he began to foment an anti-monarchy revolt through the mosques,which by 1964 resulted in imposition of martial law and finally with his arrest and his being sentenced to death by hanging. And consequently being given the life-saving ayatollah title which he had not earned.
After formally being exiled to Turkey, he ended up in Iraq where he wrote some philosophical and social behavior dissertations which were so bizarre by religious standards that, where possible, the tracts were bought up and destroyed by the Iranian Government when he took over in 1979. The most damning were in Arabic language versions and then later, cleaner texts appeared as edited translations in Farsi.
Some linguists, who studied his public speeches in 1979 and 1980, concluded his Farsi vocabulary to be less than 200 words, so not only did he not have Persian blood, he did not even speak the language. With the number of Iranians who have died because of him and his successors over the past 25 years going into the hundreds of thousands, if not well over a million if the death toll from the eight-year Iran-Iraq war is included, this Anglo-Indian with Arab Sunni Muslim theological and philosophical roots may have had no love or compassion for Iranians either.
In the Iran Air aircraft flying Khomeini back from France to Tehran in early 1979, with cameras rolling, a journalist asked: What do you feel about returning to Iran? He replied: Nothing! The question was repeated, and again he replied: Nothing!
1. Alan Peters is the nom de plume of a correspondent who spent many years engaged in security and intelligence issues in Iran. This report is copyright © 2004 by Alan Peters.
2. See Defense & Foreign Affairs Daily February 23, 2004: Iranian Elections Reinforce Short- Term Clerical Grip; Heighten Political Instability.
3. Editors note: See Defense & Foreign Affairs Daily March 1, 2004: Iranian Leadership Seeks Ways to Circumvent IAEA, and to Suppress Possible Libyan Revelations About Iranian Involvement in PA103 and WMD. Significantly, while this report deals with the concern of the Iranian clerics over the possibility of launching terrorist or insurgent attacks against Libyan leader Muammar al-Qadhafi of Libya over matters related to Irans involvement in WMD programs and the PA103 terrorist bombing, it is possible that the clerics also feel concern that the transformation of Libyas relations with the US could also reveal unpalatable truths about the disappearance of Lebanese Grand Ayatollah Mussa Sadr.
DEFENSE & FOREIGN AFFAIRS STRATEGIC POLICY 3, 2004
==================================================================
An Interview With KHOMEINI
About the Archive
This is a digitized version of an article from The Times’s print archive, before the start of online publication in 1996. To preserve these articles as they originally appeared, The Times does not alter, edit or update them.
Last month Oriana Fallaci, the Italian journalist who is noted for her provocative interviews with world leaders, journeyed to Iran in hopes of meeting with the leader of the Islamic Revolution, the Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini. For 10 days she waited in the holy city of Qum for her interview with the 79year‐old Ayatollah, who is the de facto ruler of Iran. On Sept. 12, she was led into the Faizeyah religious school, where Khomeini holds his audiences. She was accompanied by two Iranians Nyho had helped set up the interview and who served as translators. Miss Fallaci, barefoot, enveloped in a chador — the head‐to‐toe veil of the Moslem woman —was seated on a carpet; when the Ayatollah entered, the taped interview began. Miss Fallaci returned the following day for a second audience. The text on these pages is an edited transcript of the sessions.
FALLACI: Imam Khomeini, the entire country is in your hands. Every decision you make is an order. So there are many in your country who say that in Iran there is no freedom, that the revolution did not bring freedom.
KHOMEINI: Iran is not in my hands. Iran is in the hands of the people, because it was the people who handed the country over to the person who is their servant, and who wants only what is good for them. You saw very well how — after the death [at age 68, in his sleep, Sept. 10] of [Ayatollah Mahmoud] Taleghani — millions of persons went into the streets without the threat of violence. This shows that there is freedom. It also shows that the people only follow men of God. And this is freedom.
FALLACI: Forgive me if I insist, Imam Khomeini. I meant that today, in Iran, you raise fear, and many people call you a dictator. The new dictator, the new boss. The new master. How do you comment on that? Does it sadden you, or don’t you care?
KHOMEINI: On the one hand I’m sorry to hear that. Yes, it hurts me, because it is unjust and unhuman to call me a dictator. On the other hand, I couldn’t care less, because I know that wickedness is a part of human nature, and such wickedness comes from our enemies. Considering the road that we have chosen, a road that is opposed to the superpowers, it is normal that the servants of foreign interests treat me with their poison, and hurl all kinds of calumnies against me. Nor do I have any illusions that those countries which are accustomed to plundering and looting us will stand by silently and idly. Oh, the mercenaries of the Shah say lots of things — even that Khomeini ordered the breasts of women to be cut off. Tell me, since you are here, did you have any evidence that Khomeini could commit such a monstrous act, that he would cut off the breasts of women?
FALLACI: No. I did not, Imam. But you frighten people, as I said. And even this mob which calls your name is frightening. What do you feel — hearing them calling out like this, day and night, knowing that they are there, all of them there sitting for hours, being shoved about, suffering, just to see you for a moment, and to sing your praises?
KHOMEINI: I enjoy it. I enjoy hear ing and seeing them. Because they are the same ones who rose up to throw out the internal and external enemies. Because their applause is the continuation of the cry with which the usurper was thrown out. It is good that they continue to be agitated, because the enemies have not disappeared. Until the country has settled down, the people must remain fired up, ready to march and attack again. In addition, this is love, an intelligent love. It is impossible not to enjoy it.
FALLACI: Love or fanaticism, Imam? It seems to me that this is fanaticism, and of the most dangerous kind. I mean, fascist fanaticism. In fact, there are many who see a fascist threat in Iran today, and who even maintain that fascism is already being consolidated in Iran.
KHOMEINI: No, it is neither fascism nor fanaticism. I repeat, they yell like this because they love me, and they love me because they feel that I care for them, that I act for their good. That is, to apply the Commandments of Islam. Islam is justice. Dictatorship is the greatest sin in the religion of Islam. Fascism and Islamism are absolutely incompatible. Fascism arises in the West, not among people of Islamic culture.
FALLACI: Perhaps we don’t understand each other or the meaning of the word fascism, Imam. By fascism I mean a popular phenomenon, the kind we had in Italy when the crowds cheered Mussolini, as here they cheer you, and they obeyed him as they obey you now.
KHOMEINI: No. Because our masses are Moslems, educated by the clergy — that is, by men who preach spirituality and goodness. Fascism would be possible here only if the Shah were to return or if Communism were to take over. Yes, what you say could happen only if Communism would win and wipe us out. Cheering, for me, means to love freedom and democracy.
FALLACI: O.K., then. Let’s talk about freedom and democracy, Imam. And let’s do it like this. In one of your first speeches at Qum, you said that the new Islamic Government would guarantee freedom of thought and of expression for everyone, including Communists and ethnic minorities. But this promise was not kept, and now you de fine Communists as “sons of Satan,” and the leaders of the rebelling ethnic minorities as the “evil of the earth.”
KHOMEINI: First you affirm something, and then you expect me to explain your statement. You even presume that I should permit the plots of those who want to bring the country to anarchy and corruption — as though freedom of thought and of expression were the freedom to plot and to corrupt. Therefore, in answer to your question, say: For more than five months I tolerated, we tolerated, those who did not think as we do. They were free, absolutely free to do whatever they wanted. They fully enjoyed the freedom that was granted to them. I even invited the Communists to have a dialogue with us. But, in response, they burned the wheat harvest, they burned the urns of the electoral offices, and they reacted to our offer for a dialogue with rifles and arms. In fact, they were the ones who stirred up the problem of the Kurds. Thus, we understood that they were taking advantage of our tolerance to sabotage us, that they did not want freedom but the license to subvert, and we decided to stop them. And when we discovered that — urged on by the former regime and foreign forces — they were seeking our destruction with other plots and other means, we shut them up
FALLACI: For example, by closing the newspapers of the opposition. In that speech at Qum you also said that to be modern means to form men who have the right to choose, and to criticize. But the liberal newspaper Ayandegan was shut down. And so were all the leftist newspapers.
KHOMEINI: The newspaper Ayandegan was part of the plot I mentioned. It had relations with the Zionists; it got ideas from them to do harm to the country. The same goes for all the newspapers that the attorney general of the revolution judged subversive, and then closed: newspapers which, through a phony opposition, tried to restore the old regime and to serve foreign interests. We shut them up because we knew who they were, and what they were after. And this is not contrary to freedom. This is done everywhere.
FALLACI: No, Imam, it is not. In any event, how can you call those who fought against the Shah, who were persecuted, arrested and tortured by him, as being “nostalgic for the Shah’? How can you call them enemies, how can you deny them a place and the right to exist, those leftists who fought and suffered so much?
KHOMEINI: None of them fought or suffered. If anything, they took advantage of the anguish of the people who fought and suffered. You are not very well informed. A good part of the left which you refer to was abroad during the imperial regime, and came back only after the people had overthrown the Shah. Another group was here, it is true, hidden in their clandestine coves and in their houses. It was only after the people had shed their blood that these leftists came out to take advantage of that blood. But until now nothing has happened to limit their freedom.
FALLACI: Imam, I want to make sure that I understand correctly. You say that the left had no part in the overthrow of the Shah. Not even that seg ment of the left that had so many people arrested, so many tortured, so many martyred. So, on the left, nobody counts, neither the living nor the dead.
KHOMEINI: They did not contribute anything. They did not help the revolution at all. Some of them fought, yes, but only for their ideas, only for their goals, only for their interests. They were not decisive for the victory, they were not responsible, they did not contribute anything. No, the left never cooperated with us, they only gave us problems. During the Shah’s regime they were against us as much as they are now, so much so that their hostility toward us was worse than that of the Shah himself, much deeper. It is not by chance that the present plot comes from them. My view is that it is not even a real left, but an artificial left, created by the Americans.
FALLACI: Do you mean a left made in the United States, Imam?
KHOMEINI: Yes, created and supported by the Americans to launch plundering against us, to sabotage and destroy us.
FALLACI: So, when you speak of “the people,” you refer exclusively to the people connected with the Islamic movement. And I ask you: The people who were killed by the tens of thousands, did they die for freedom, or for Islam?
KHOMEINI: For Islam. The people fought for Islam. And Islam means everything, also those things that, in your world, are called freedom, democracy. Yes, Islam contains everything. Islam includes everything. Islam is everything.
FALLACI: At this point, Imam, must ask you what you mean by freedom.
KHOMEINI: Freedom; it is not easy to define this concept. Let us say that freedom is when you can choose your own ideas and think about them when you please, without being forced to think something else. Let’s say that freedom is to live where you want, and to do the work that you like.
FALLACI: To think, not to express, or to make your thoughts concrete? And by democracy, what do you mean, Imam? I’m asking this question with much curiosity because — in the [March 1979] referendum on whether there was to be a republic or a monarchy — you prohibited the expression “Islamic Democratic Republic.” You banned the word democratic, saying, “Not a word more, not a word less.” As a result, the people who believe in you use the term “democracy” as though it were a dirty word. What’s wrong with this noun, which seems so beautiful to us in the West?
KHOMEINI: To begin with, the word Islam does not need adjectives such as democratic. Precisely because Islam is everything, it means everything. It is sad for us to add another word near the word Islam, which is perfect. Besides, this democracy, which you love so much and that you consider so valuable, does not have a precise meaning. Aristotle’s democracy is one thing, the Soviet democracy is another thing, the democracy of the capitalists is still another. We cannot afford to have such an ambiguous concept placed in our Constitution. Finally, let me give you a historical example, to show you what mean by democracy. When All [the seventh‐century Imam whom Shiite Moslems believe to be the first rightful Moslem leader] succeeded the Prophet, and became head of the Islamic state — and this consideration had all the power, and his reign extended from Saudi Arabia to Egypt, and included a large part of Asia and also of Europehe happened to have a dispute with a Jew. And the Jew had him called by the judge, and All accepted the summons of the judge, and went to him. And when be entered the room, the judge stood up, but All said to him angrily, “Why do you stand up when I enter the room but not when the Jew entered? Before a judge the two contending parties should be treated the same way.” Afterward, he accepted the sentence, which was unfavorable to him. I ask you, you who have traveled and seen all forms of government and know history, can you give me a better example of democracy?
FALLACI: Imam, democracy means much more than that. This is said by many Iranians, too. The same Iranians who don’t understand the direction where your Islamic Republic is going.
KHOMEINI: If you foreigners do not understand, too bad for you. It’s none of your business, you have nothing to do with our choices. If some Iranians don’t understand it, too bad for them. It means that they have not understood Islam.
FALLACI: Well, they certainly understand despotism practiced by clergy today, Imam. In drafting the new Constitution, the assembly of experts passed one article, the fifth principle, by which the head of the country will have to be the supreme religious authority. That is, you. And the supreme decisions will be made only by those who know the Koran well. That is, the clergy. Doesn’t this mean that, according to the Constitution, politics will continue to be determined by the priests and no one else?
KHOMEINI: This law, which the people will ratify, is in no way in contradiction with democracy. Since the people love the clergy, have faith in the clergy, want to be guided by the clergy, it is right that the supreme religious authority should oversee the work of the Prime Minister or of the President of the republic, to make sure that they don’t make mistakes or go against the law: that is, against the Koran. It can be either the supreme religious authority, or a representative group of the clergy.
FALLACI: Let’s consider for a moment the justice administered by the clergy, Imam. Let’s talk about the 500 executions that took place in Iran after the victory. Do you approve of the summary way in which these trials are taking place, without lawyers, without the chance for an appeal?
KHOMEINI: Evidently in the West you ignore, or you pretend to ignore, who was being executed. They were persons who participated in massacres in the streets and the squares, or persons who ordered those massacres, or persons who burned down homes, who tortured, who cut off the arms and legs of those who were being interrogated. What should we have done with them, granted pardons and let them go free? The right to defend themselves, and to respond to accusations — we gave them those chances. But once their guilt was demonstrated, what need was there, or is there, for an appeal? Write the trary if you want, the pen is in your hand. My people do not ask your questions. And I will even go farther: had we not executed those criminals, the revenge of the people would have gone beyond control. Every functionary employee of the regime would have been executed. And the dead would have numbered far more than 500. They would have been in the thousands.
FALLACI: All right, but !did not necessarily mean the tortures and the Savak killers; Imam. I meant • those who were executed and had nothing to do with the regime, the people who are still being shot today for adultery, or prostitution, or homosexuality. Is it right to shoot the poor prostitute or a woman who is unfaithful to her husband, or a man who loves another man?
KHOMEINI: If your finger suffers from gangrene, what do you do? Do you let the whole hand, and then the body, become filled with gangrene, or do you cut the finger off? What brings corruption to an entire country and its people must be pulled up like the weeds that infest a field of wheat. I know there are societies where women are permitted to give themselves to satisfy the desire of men who are not their husbands, and where men are permitted to give themselves to satisfy other men’s desires. But the society that we want to build does not permit such things. In Islam, we want to implement a policy to purify society, and in order to achieve this aim we must punish those who bring evil to our youth. Don’t you do the same? When a thief is a thief, don’t you throw him in jail? In many countries, don’t you even execute murderers? Don’t you use that system because, if they were to remain free and alive, they would contaminate others and spread
FALLACI: Imam, how is it possible to compare a Savak murderer and torturer with a citizen who exercises his sexual freedom? Take the example of the boy they shot yesterday, for sodomy.
KHOMEINI: Corruption, corruption. We have to eliminate corruption.
FALLACI: Take the case of the pregnant 18-year-old girl who was shot at Beshar a few weeks ago, for adultery.
KHOMEINI: Pregnant? Lies, lies. Lies like those about cutting off the breasts of women. In Islam, these things do not happen. We do not shoot pregnant women in Islam.
FALLACI: They are not lies, Imam. All the Iranian newspapers reported the news, and a debate was held on television because her lover was only given a hundred lashes.
KHOMEINI: If that is true, it means that she got what she deserved. What do I know about particulars? The woman must have done something more serious. Ask the court that condemned her. Stop talking about these things. I am getting tired. These are not important matters.
FALLACI: Then let’s talk about the Kurds who are being executed because they want autonomy.
KHOMEINI: The Kurds who are being executed do not belong to the Kurdish people. They are subversives who are acting against the people and against the revolution, such as the one who was shot by a firing squad yesterday. He had killed 13 people. I would prefer it if no one had to be executed, but when someone like the person they caught is shot, it makes me feel good.
FALLACI: And what about when persons are arrested, like the five this morning, because they were distributing Communist handouts?
KHOMEINI: If they were arrested was because they deserved it, because they were serving a foreign interest, like the phony Communists who act on behalf of America, and of the Shah. Enough. I’ve said enough about these things.
FALLACI: O.K., Imam. Let’s talk about the Shah. Was it you, Imam, who gave the order to have the Shah executed abroad, and who said that whoever performed this feat would be considered a hero, and if he were to be killed during the operation, he would go to heaven?
KHOMEINI: No! Not I. Because want the Shah brought to Iran to stand trial in public, for 50 years of crimes against the Persian people, including the crimes of treason and robbery. If he were killed abroad, that money would be lost. And if, instead, we Judge him here, we can get that money back. No, no, I do not want him to be killed abroad. I want him here, here. And in order to make it happen, I pray for his health, just as the Ayatollah [Kazem Shariat‐] Madari prayed for the health of Riza Pahlevi, the father of this Pahlevi, who also fled the country with a lot of money.
FALLACI: But if the Shah returned the money, would you stop the hunt?
KHOMEINI: For the money, if he really returned it, yes. But with regard to the treason against this country, and against Islam, no. How can he be forgiven for the massacre of 16 years ago — or the Black Friday massacre of one year ago? How can he be forgiven for all the death he left behind? Only if the dead were to come back to life could pardon him, and accept the money.
FALLACI: And in order to bring him back to Iran, there would be an operation similar to the one which led to the capture of Eichmann in Argentina, suppose. Does it apply only to the Shah or to his family as well?
KHOMEINI: He who has committed crime Is guilty. If the family did not participate in any crime I do not see why they should be condemned. Belonging to the Shah’s family is no crime in itself. His son Riza, for example, did not dirty himself by any crimes, as far as 1 know. Thus, I have nothing against him. He can return to Persia, to Iran, whenever he wants, and live here as a normal citizen. Let him come back.
FALLACI: I say he won’t come back, Imam. And what about Farah Diba [the Shah’s wife]?
KHOMEINI: The tribunal will decide about her.
FALLACI: And Ashraf [Princess Ashraf Pahlevi, the Shah’s sister]?
KHOMEINI: Ashraf is the evil twin of the Shah, a traitoress, just like the Shah. And for the crimes she committed, she must be prosecuted and condemned Just as the Shah.
FALLACI: And the former Prime Minister, [Shahpur] Bakhtiar? [Bakhtiar disappeared last Feb. 12.] Bakhtiar says that he will return to his position, Imam, that he already has a Government to substitute for this Government.
KHOMEINI: If Bakhtiar should be executed or not, I cannot say as yet. But I do know that he must be prosecuted. Let him come back, let him come back, even with his new Government. Let him come back, even arm‐in‐arm with the Shah. Thus, they would end up in court together. Yes, I must admit that would very much like to see Bakhtiar together with the Shah, hand‐in‐hand. I’m looking forward to it.
FALLACI: Death to Bakhtiar also, therefore. Imam Khomeini, haven’t you ever forgiven anyone? Have you ever felt pity, sympathy for someone? And while we are at it, have you ever cried?
KHOMEINI: I cry, I laugh, I suffer. Do you think I’m not a human being? With regard to forgiving: I pardoned the majority of those who caused us harm. I granted an amnesty to the police, to the gendarmes, to a lot of people. That is, to those who were not involved in torture or serious crimes. just granted an amnesty to the rebel Kurds. Thus I believe that I have demonstrated pity. But for those that we discussed before, there is no pardon, there is no pity. Now that’s enough. am tired, that’s enough.
FALLACI: Please, ‘mam, there are many things I still want to ask you. For example, this chador that they made me put on, to come to you, and which you insist all women must wear. Tell me, why do you force them to hide themselves, all bundled up under these uncomfortable and absurd garments, making it hard to work and move about? And yet, even here, women have demonstrated that they are equal to men. They fought just like the men, were imprisoned and tortured. They, too, helped to make the revolution.
KHOMEINI: The women who contributed to the revolution were, and are, women with the Islamic dress, not elegant women all made up like you, who go around all uncovered, dragging behind them a tail of men. The coquettes who put on makeup and go into the street showing off their necks, their hair, their shapes, did not fight against the Shah. They never did anything good, not those. They do not know how to be useful, neither socially, nor politically, nor professionally. And this is so because, by uncovering themselves, they distract men, and upset them. Then they distract and upset even other
FALLACI: That’s not true, Imam. In any case, I am not only talking about piece of clothing, but what it represents. That is, the condition of segregation into which women have been cast once again, after the revolution. The fact that they can’t study at university with men, or work with men, for example, or go to the beach or to a swimming pool with men. They have to take a dip apart, in their chadors. By the way, how do you swim in a chador?
KHOMEINI: This is none of your business. Our customs are none of your business. If you do not like Islamic dress you are not obliged to wear it. Because Islamic dress is for good and proper young women.
FALLACI: That’s very kind of you, Imam. And since you said so, I’m going to take off this stupid, medieval rag right now. There. Done. But tell me something. A woman such as I, who has always lived among men, showing her neck, her hair, her ears, who has been in war and slept in the front line in the field among soldiers, according to you, is she an immoral, bold and unproper woman?
KHOMEINI: Your conscience knows the answer. I do not judge personal matters, I cannot know whether your life is moral or immoral, whether you behaved properly or not with the soldiers at the front. But I do know that, during my long lifetime, I have always been right about what I said. If this piece of clothing did not exist — the Islamic dress — women could not work in a useful and healthy way. And not even men. Our laws are valid laws.
FALLACI: Even if the law permits man to have four wives, Imam?
KHOMEINI: The law of the four wives is a very progressive law, and was written for the good of women, since there are more women than men. More women are born than men, and more men are killed in war than women. A woman needs a man, so what can we do, since there are more women than men in the world? Would you rather prefer that the excess number of women became whores — or that they married a man with other wives? And let me add another point. Even under the difficult conditions which Islam imposes on a man with two or three or four wives, there is equal treatment, equal affection, and equal time; this law is better than monogamy.
FALLACI: But you are talking about laws and customs that go back 1,900 years ago, Imam Khomeini. Doesn’t seem to you that the world has progressed since then? In observance of those laws, you have even resurrected the prohibition against music and alcohol. Tell me, why is it a sin to drink a glass of wine or beer, when you are thirsty or when you’re eating? And why is listening to music a sin? Our priests drink and sing — even the Pope. Does this mean the Pope is a sinner?
KHOMEINI: The rules of your priests do not interest me. Islam prohibits alcoholic drinks and that’s all. It prohibits them in an absolute way, because drinking makes pet de lose their heads and impedes clear thinking. Even music dulls the mind, because involves pleasure and ecstasy, simi:ar to drugs. Your music, I mean. Usually your music has not exalted the spirit, it puts it to sleep. And it destructs our youth, who become poisoned by it, and then they no longer care about their country.
FALLACI: Even the music of Bach, Beethoven, Verdi?
KHOMEINI: I do not know those names. If their music does not dull the mind, they will not be prohibited. Some of your music is permitted. For example, marches and hymns for marching. We want music that lifts the spirit, as in marches, music that makes our youth move instead of paralyzing them, music that helps them to care about their country. Yes, but your marches are permitted.
FALLACI: Imam Khomeini, you always use harsh terms when speaking of the West. Any judgment you express about us draws the conclusion that you view us as champions of every kind of ugliness, every kind of perversion. And yet you were accepted by the West when you went into exile, and many of your associates started in the West. Doesn’t it appear to you that there is also something good about us?
KHOMEINI: Something, yes. Something. But when we have been bitten by a snake, we are even afraid of a piece of rope which from afar looks like a snake. And you have bitten us too much, and too long. You only saw in us a market, and that was all. You only exported bad things to us, and that was all. The good things, such as material progress, you kept such things for yourself. Yes, we got many bad things from the West, a lot of suffering, and now we have good reasons to fear the West, to keep our youth from getting too close to the West and being influenced even more by the West. No, I do not want our youth to go and study in the West, where they become corrupted by alcohol, by the music that blocks out thought, by drugs and uncovered women. To say nothing of the fact that our youth are not given the same treatment as your youth in the West. You give our youth a diploma even if they
FALLACI: Yes, Imam, but the airplane that brought you back to your country is a product of the West — even the telephone that you use to communicate with, from Qum, even the television set that you so often use to convey messages to the country, even this airconditioner, which permits you to remain cool in this desert. If we are so corrupt and so corrupting, why do you use our evil tools?
KHOMEINI: Because these are the good things from the West. And we are not afraid to use them, and we do. We are not afraid of your science and of your technology. We are afraid of your ideas and of your customs. Which means that we fear you politically and socially. And we want this to be our country. We do not want you to interfere anymore in our politics and our economy, in our habits, our affairs. And from now on, we will go against anyone who tries to interfere — from the right or from the left, from here or from there. And now that’s enough. Go away. Go away.
FALLACI: One last question, Imam. During these days that I have been in Iran, I have noticed a lot of discontent, a lot of disorder and chaos. The revolution has not brought the good fruits it promised. The country is sailing in dark waters, and there are some who see very difficult times for Iran. There are even those who foresee a development of the conditions for a civil war, or a coup d’état. What do you think?
KHOMEINI: I shall say this. We are like the child that is only six months old. Our revolution is only six months old. And it is a revolution that took place in a country that was eaten alive like a field of wheat infested with locusts. We are at the beginning of our road. What do you expect of a child that is six months old, born in a field filled with locusts, after 2,500 years of bad harvests and 50 years of poisonous harvests? That past cannot be wiped out in a few months, not even in a few years. We need time. We ask for time. And, above all, we address ourselves to those who call themselves Communists, or democrats, or God knows what. They are the ones who do not want to give us time. They are the ones who attack us, and spread around talk of civil wars and coups which won’t take place because the people are united. They are the ones who are spreading chaos. Those who call themselves Communists and democrats and God knows what, 1 repeat. Now, goodbye. Inshallah.
====================================================================
